Data and Logistic Growth
Does Data Represents Logistic Growth?
Logistic Growth
A pond has duckweed growing on its surface. As the duckweed continues to grow, resources become limited. The limitations cause the growth rate to change. What we see is constrained or logistic growth.
![]() The differential equation to describe constrained or logistic growth is:
The differential equation to describe constrained or logistic growth is:
where P represents the population, t represents time, k is a constant related to the rate of growth, and M is a constant that represents the maximum sustainable population. In this differential equation as the value of P is near zero and the value of M-P is near M, the rate of change is similar to normal exponential growth. As the value of P nears M, the rate of change nears zero. This behavior creates a curve with the familiar "S" shape that describes logistic growth.
The solution to this differential equation is
![]() where P0 is the constant of integration. Looking at this equation does not provide the same intuition about the kind of growth of the population as is given in the differential equation.
where P0 is the constant of integration. Looking at this equation does not provide the same intuition about the kind of growth of the population as is given in the differential equation.
Data and Derivatives: The Difference Quotient
The difference quotient can be used to describe the rate of change in data. Given data
|
t0 |
t1 |
t2 |
t3 |
t4 |
t5 |
|
P0 |
P1 |
P2 |
P3 |
P4 |
P5 |
![]() which represents a phenomenon. To estimate the slope of the tangent line of the function that represents this data find the value of
which represents a phenomenon. To estimate the slope of the tangent line of the function that represents this data find the value of
for each pair of data point.
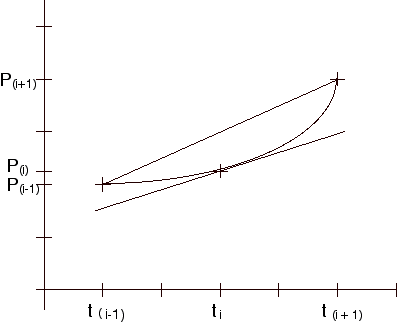 If this value is associated with the point ti, the resulting pairs of data points estimate the derivative of the function.
If this value is associated with the point ti, the resulting pairs of data points estimate the derivative of the function.
Is the Data Logistic?
To explore whether data can be described by a logistic function, we will combine the difference quotient with the differential equation.
The differential equation
![]()
![]() can be rewritten as
can be rewritten as
![]() When the ordered pairs
When the ordered pairs
are graphed, the graph is linear with a slope —k and an intercept of kM.
Possible Link: Test the ideas
![]() Using the difference quotients to represent the values of dP/dt , the ordered pairs
Using the difference quotients to represent the values of dP/dt , the ordered pairs
should be linear. If so, the slope and the vertical intercept of the data can help us find the constants of differential equation.
Summary of Steps to Investigate Logistic Data
Try Out Using Maple