|
|
|
|
|
|
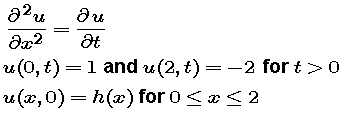
The initial condition h is graphed below

Show that w is the unique steady-state solution of the heat equation with the boundary conditions w(0) = 1 and w(2) = -2, i.e., the unique function satisfying the heat equation, the boundary conditions, and the condition that the partial derivative of w with respect to t is 0.
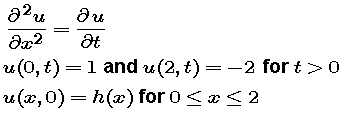 .
.
is a solution of

|
|
|